
All these interactions are sent in a streaming manner for the ETL engine to process and transform into an analyzable format. In such a scenario, a customer might be using the business’ services (such as a cell phone or a streaming video service) and also searching on their website for support. One example of the use of streaming ETL is in a “360-degree customer view” use case, especially one that enhances real-time interactions between the business and the customer. They must respond to new data in real-time as the data is generated. Streaming ETL: Real-time applications require streaming ETL. Fraud detection, Internet of Things, edge computing, streaming analytics, and real-time payment processing are examples of applications that rely on streaming ETL. These real-time applications require streaming ETL.
#ETL PROCESSES SOFTWARE#
Batch ETL: In traditional data environments, ETL software extracted batches of data from a source system usually based on a schedule, transformed that data, then loaded it to a repository such as a data warehouse or database. They must respond to new data in real time as the data is generated. However, many modern business environments cannot wait hours or days for applications to handle batches of data. In traditional data environments, ETL software extracted batches of data from a source system usually based on a schedule, transformed that data, then loaded it to a repository such as a data warehouse or database.

In some streaming technology circles, the originating system is called a source, and the destination is called a sink. In streaming ETL, this entire process occurs against streaming data in real time in a stream processing platform. Load refers to sending the processed data to a destination, such as a database. During this process, the data may be cleansed and prepared for use in your business systems or processes.
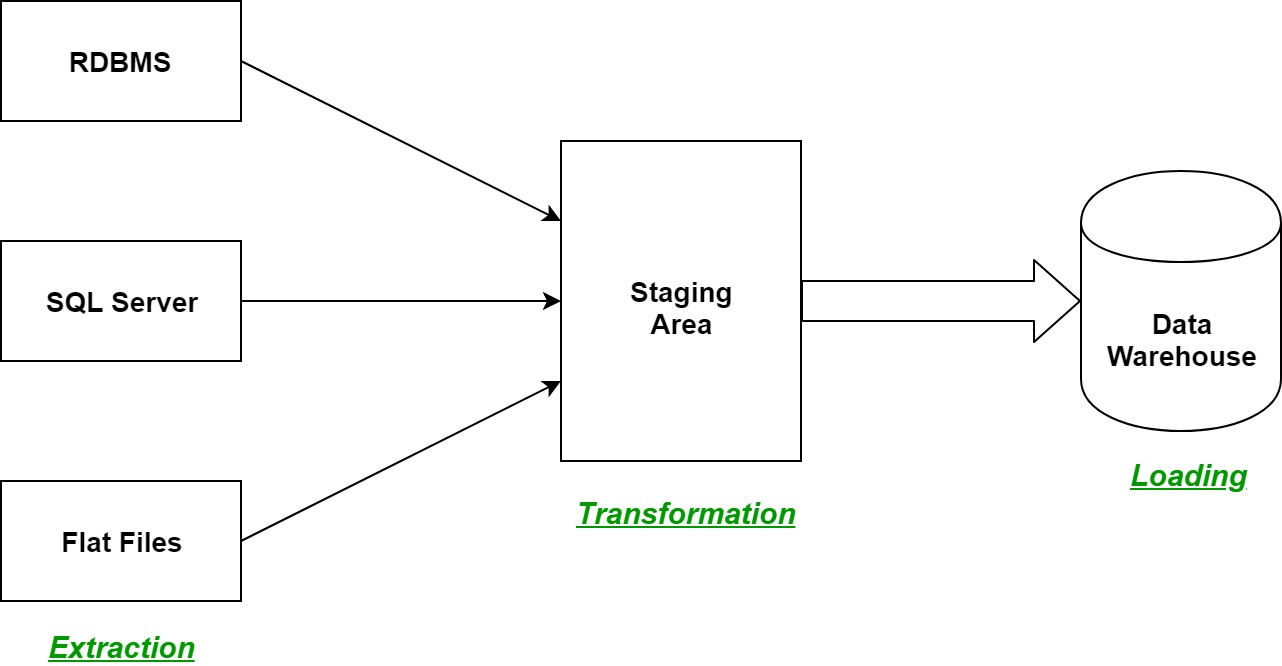
Once data has been extracted from the data source, the transform process converts the data into a format that can be used by different applications. Transform refers to any processes performed on that data. These data sources could be legacy business systems, traditional databases, IoT devices, sensor data, APIs, and so on. How Does Traditional ETL Work?įirst, a little background on traditional ETL: ExtractĮxtract refers to collecting data from some data source. ETL is short for the database functions extract, transform, and load. Streaming ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is the processing and movement of real-time data from one place to another.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
